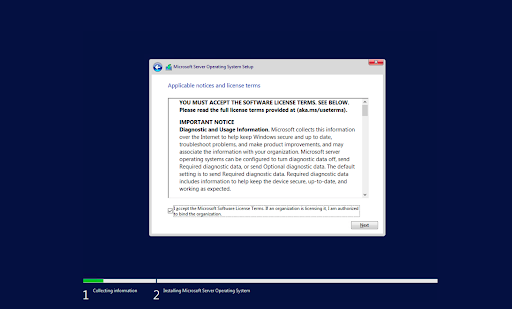
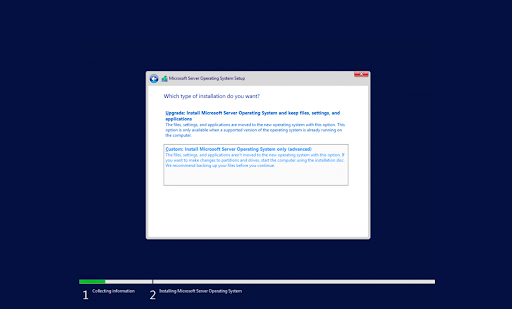
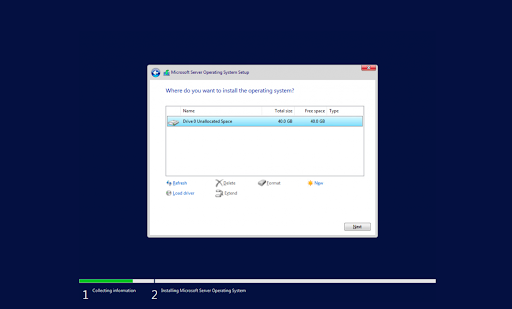
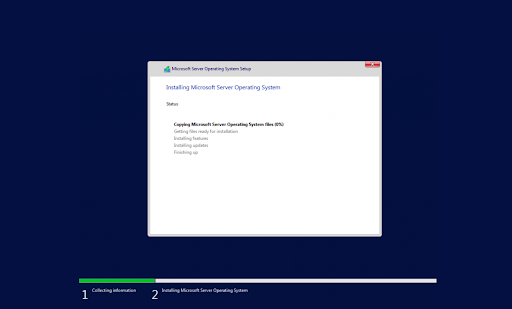
Trước đây được biết đến với cái tên
Windows Server Virtualization và tên mã Viridian, Hyper-V là công nghệ ảo hoá server thế hệ mới của
Microsoft và là thành phần quan trọng trong HĐH
Windows Server 2008 sắp ra mắt.
Trước đây được biết đến với cái tên Windows Server Virtualization và tên mã Viridian, Hyper-V là công nghệ ảo hóa server thế hệ mới của Microsoft và là thành phần quan trọng trong hệ điều hành Windows Server 2008 sắp ra mắt.Tổng quan
Microsoft không là tay mơ trong lĩnh vực ảo hóa, đặc biệt là ảo hóa máy chủ. Sản phẩm Virtual Server (cùng với sản phẩm ảo hóa desktop -
Virtual PC) của hãng đã xác lập chỗ đứng trên thị trường từ nhiều năm nay. Trên nền công nghệ ảo hóa truyền thống, phiên bản 2005 hiện tại của Virtual Server đã tột bậc, ít nhất là đối với Microsoft, và sẽ không có thêm phiên bản mới nào nữa (và cũng sẽ không có thêm sản phẩm ảo hóa phía server 32-bit mới nào khác). Tuy nhiên,
Virtual Server 2005 vẫn có thể làm việc trên Windows Server 2008 (WS08) và sẽ được hỗ trợ đến hết năm 2014.
| | "Hiện nay, trên toàn cầu, chưa đến 4% máy chủ có ứng dụng công nghệ ảo hóa, trong khi đó chưa đến 1/10 máy chủ đang chạy chỉ ở 10% công suất. Trong tương lai, hơn một nửa máy chủ sẽ được ảo hóa", Andrew Lees, phó chủ tịch nhóm giải pháp và tiếp thị máy chủ và công cụ của Microsoft. | |
Hyper-V chính là công nghệ ảo hóa thế hệ kế tiếp dựa trên hypervisor, khai thác phần cứng server 64-bit thế hệ mới (Hyper-V chỉ chạy trên nền HĐH server 64-bit và CPU 64-bit có tính năng ảo hoá) và có nhiều cải tiến quan trọng, là thành phần quan trọng trong WS08 và tích hợp với các công cụ quản lý server quen thuộc trên Windows. Người dùng (chủ yếu là doanh nghiệp) không cần phải mua thêm phần mềm để khai thác các tính năng ảo hoá. Kiến trúc mở của Hyper-V cho phép các nhóm phát triển nội bộ và các nhà phát triển phần mềm của hãng thứ ba cải tiến công nghệ này và các công cụ.
Với Hyper-V, Microsoft cung cấp một nền tảng ảo hóa mạnh và linh hoạt, có thể đáp ứng nhu cầu ảo hóa mọi cấp độ cho môi trường doanh nghiệp (
DN).
Ảo hóa linh hoạt
Hyper-V là thành phần trong chiến lược ảo hóa datacenter-đến-desktop của Microsoft, các tính năng ảo hóa server của Hyper-V có thể giúp ích không chỉ cho server ở qui mô công ty với hàng trăm hay hàng ngàn máy trạm, mà còn cả server trong các văn phòng nhỏ.
Hyper-V cho phép các máy ảo khai thác lượng bộ nhớ rất lớn, các bộ xử lý đa nhân mạnh mẽ, các giải pháp lưu trữ động, và thế hệ mới của mạng tốc độ cao. Điều đó có nghĩa ngay cả những ứng dụng máy chủ quan trọng cần nhiều tài nguyên cũng trở thành những ứng viên khả thi cho việc hợp nhất và ảo hóa thay vì yêu cầu các server dành riêng.
Mặt khác, DN có thể hợp nhất các server của chi nhánh nhỏ nhờ các tính năng của Hyper-V và System Center, như giám sát và quản lý tập trung, sao lưu tự động và các công cụ quản lý khác. Điều này cho phép các văn phòng chi nhánh hoạt động mà không cần có bộ phận IT tại chỗ.
System Center có thể tăng tính linh hoạt của hệ thống bằng cách chuyển các server vật lý thành các server trên máy ảo. Ví dụ, tính năng chuyển đổi vật lý sang ảo của
System Center Virtual Machine Manager cho phép người quản trị chuẩn hóa nền tảng phần cứng server và chuyển một số ứng dụng nghiệp vụ sang máy ảo với thời gian gián đoạn tối thiểu. Với các công cụ giám sát của System Center, quá trình này có thể thực hiện tự động theo cách thức do người quản trị quyết định.
Nền tảng ảo hóa mạnh
Các máy ảo có thể tận dụng các tính năng liên cung (cluster), sao lưu và bảo mật mạnh trong Windows Server 2008 để vận hành trơn tru, vượt qua các tình huống tải tăng đột xuất hay sự cố. Hyper-V sử dụng các dịch vụ
Volume Shadow Copy của Windows Server 2008 để cho phép khắc phục sự cố nhanh và tin cậy, đưa các ứng dụng nghiệp vụ trở lại làm việc với thời gian gián đoạn tối thiểu, ngay cả sau khi xảy ra thiên tai hay lỗi phần cứng.
Liên cung chủ dùng nhiều server vật lý giúp giảm thiểu ảnh hưởng có thể của lỗi server. Liên cung khách dùng nhiều máy ảo cung cấp hình thức bảo vệ tương tự cho các máy ảo cũng như cân bằng tải bên trong một server vật lý duy nhất. Hyper-V hỗ trợ việc tạo liên cung chủ và khách, cho phép triển khai các cấu hình mạng linh hoạt và chắc chắn hơn.
Hyper-V còn cho phép di chuyển nhanh các máy ảo đến server khác, tự động hay thủ công, với thời gian gián đoạn hoạt động tối thiểu.
| VIRTUAL SERVER 2005 VS. HYPER-V | |
| Tính năng ảo | | | Visual Server 2005 R2 | | | Hyper-V | |
| Máy ảo 32 bit | | | Yes | | | Yes | |
| Máy ảo 64 bit | | | No | | | Yes | |
| Máy ảo đa bộ xử lý | | | No | | | Yes, 4 core VMs | |
| Hỗ trợ bộ nhớ máy ảo | | | 3.6 GB/VM | | | 32 GB/VM | |
| Quản lý bởi System Center Virtual Machine Manager | | | Yes | | | Yes | |
| Hỗ trợ cho Microsoft Clustering Services | | | Yes | | | Yes | |
| Hỗ trợ sao lưu ở máy chính | | | Yes | | | Yes | |
| Lập trình/ Mở rộng | | | Yes, COM | | | Yes, WMI | |
| Giao diện người dùng | | | Web Interface | | | MMC 3.0 Interface | |
Tăng cường bảo mật
Bảo mật là thách thức quan trọng trong mọi giải pháp server, dù là vật lý hay ảo. Các máy chủ chứa hệ thống ảo hóa cũng có thể bị “mở toang” như server độc lập, nếu không quản lý sẽ làm suy yếu tính bảo mật của các máy ảo. Hyper-V tăng cường tính bảo mật cho cả máy chủ chính và máy ảo theo nhiều cách.
Hyper-V cho phép các máy ảo khai thác những tính năng bảo mật cấp phần cứng có trên các server trang bị thế hệ bộ xử lý mới nhất. Ví dụ, tính năng “thực thi bit cấm” có thể nhận biết các cuộc tấn công kiểu virus phổ biến và ngăn chặn được nhiều loại virus không cho chiếm quyền điều khiển hệ thống, gây quá tải hệ thống và phát tán đến các máy khác.
Server dùng chung cho nhiều người quản trị cũng có thể tránh được các nguy cơ bảo mật. Hyper-V cung cấp tính năng bảo mật dựa trên "role" (vai trò) mạnh kết hợp Active Directory và Group Policy, tránh mở toang các máy ảo thông qua server dùng chung. Ví dụ, một hệ thống có thể thiết lập để người quản trị hệ thống kế toán không thể cấu hình lại máy chủ mail.
Bằng cách tích hợp với các công cụ bảo mật mạng chuẩn mực, Hyper-V cho phép người quản trị thiết lập cùng mức bảo vệ cho các máy ảo như với các server vật lý. Các máy ảo có thể sử dụng Windows Firewall và Network Access Protection Policies giống như các server vật lý.
Bản thân kiến trúc của Hyper-V đã có lợi cho bảo mật. Với việc tối thiểu mã lệnh cho thành phần hypervisor, kết hợp với tùy chọn cài đặt Server Core của WS08, Hyper-V có thể thu nhỏ rất nhiều “bề mặt tấn công” mà virus và các loại mã độc có thể khai thác.
Ứng dụng
Lợi ích phổ biến nhất của ảo hóa là hợp nhất server, cho phép 1 server đảm đương nhiều công việc của nhiều server; ví dụ hợp nhất mail server, web server, print server... Ngoài việc giảm chi phí mua hay thuê phần cứng server, ảo hóa còn giúp giảm chi phí liên quan đến xử lý nhiệt, điện năng tiêu thụ, không gian và bảo trì.
Hyper-V có thể làm được nhiều hơn thế. Nó còn giúp cải thiện độ tin cậy mạng, khả năng mở rộng, tính bảo mật và tính linh hoạt. Là thành phần trong chiến lược ảo hóa datacenter-đến-desktop của Microsoft, Hyper-V giúp cho doanh nghiệp trong 4 vấn đề quan trọng: hợp nhất server, liên tục hoạt động và khôi phục sau thảm họa, thử nghiệm và phát triển, trung tâm dữ liệu động. Kết hợp với công cụ System Center, DN có được giải pháp hợp lý tích hợp và hoàn chỉnh làm việc với các server vật lý và máy ảo.
Hợp nhất server
DN hiện nay chịu áp lực giảm nhẹ việc quản lý và cắt giảm chi phí trong khi duy trì và nâng cao ưu thế cạnh tranh như tính linh hoạt, độ tin cậy, khả năng mở rộng và bảo mật. Công dụng cơ bản của ảo hóa cho phép hợp nhất nhiều server trên 1 hệ thống duy nhất trong khi duy trì sự cách ly giúp giải quyết những yêu cầu trên. Một trong những lợi ích chính của việc hợp nhất server là tổng phí sở hữu thấp hơn, không chỉ từ việc giảm các yêu cầu phần cứng mà còn từ chi phí điện năng, làm mát và chi phí quản lý. Một lợi ích khác là từ việc tối ưu hệ thống hạ tầng, cả từ quan điểm hiệu quả sử dụng tài sản cũng như khả năng cân bằng tải xuyên suốt nhiều tài nguyên khác nhau. Một lợi ích phụ của việc hợp nhất server là tính linh hoạt được cải thiện của môi trường chung và khả năng kết hợp tải 32-bit và 64-bit trong cùng môi trường.
| | KIẾN TRÚC HYPER-V
Hyper-V gồm 3 thành phần chính: hypervisor, ngăn ảo hóa và mô hình I/O (nhập/xuất) ảo hóa mới. Hypervisor là lớp phần mềm rất nhỏ hiện diện ngay trên bộ xử lý (BXL) theo công nghệ Intel-V hay AMD-V (xem bài “Hiện thực ảo hóa”, ID: A0607_127), có vai trò tạo các "partition" (phần vùng) mà thực thể ảo sẽ chạy trong đó.
Một partition là một đơn vị cách ly về mặt luận lý và có thể chứa một hệ điều hành làm việc trong đó. Luôn có ít nhất 1 partition gốc chứa Windows Server 2008 và ngăn ảo hóa, có quyền truy cập trực tiếp các thiết bị phần cứng. Partition gốc tiếp theo có thể sinh các partition con (được gọi là máy ảo) để chạy các HĐH khách. Một partition con cũng có thể sinh tiếp các partition con của mình.
Máy ảo không có quyền truy cập đến BXL vật lý, mà chỉ “nhìn thấy” BXL được hypervisor cấp cho. Máy ảo cũng chỉ sử dụng được thiết bị ảo, mọi yêu cầu đến thiết bị ảo sẽ được chuyển qua VMBus đến thiết bị ở partition cha. Thông tin hồi đáp cũng được chuyển qua VMBus. Nếu thiết bị ở partition cha cũng là thiết bị ảo, nó sẽ được chuyển tiếp cho đến khi gặp thiết bị thực ở partition gốc. Toàn bộ tiến trình trong suốt đối với HĐH khách.
Hyper-V được tích hợp sẵn trong HĐH Windows Server, và hypervisor móc trực tiếp đến các luồng xử lý của BXL, nhờ vậy việc vận hành máy ảo hiệu quả hơn so với kiến trúc ảo hoá trước đây. | |
|
| |
Liên tục hoạt động và khôi phục sau thảm họa
Tính liên tục hoạt động là khả năng giảm tối thiểu thời gian ngưng hoạt động cả theo lịch lẫn đột xuất, bao gồm thời gian bị mất cho các thủ tục như bảo trì và sao lưu, cũng như những mất mát không lường được. Hyper-V có các tính năng đảm bảo hệ thống hoạt động như sao lưu trực tiếp và “di cư” nhanh, đáp ứng những tiêu chuẩn về thời gian hoạt động và đáp ứng.
Khôi phục sau thảm hoạ là một thành phần quan trọng của tính liên tục hoạt động. Các thảm hoạ tự nhiên, các cuộc tấn công mã độc, thậm chí các vấn đề cấu hình đơn giản như đụng độ phần mềm đều có thể làm tê liệt các dịch vụ hệ thống cho đến khi người quản trị khắc phục sự cố và khôi phục dữ liệu đã sao lưu. Khai thác khả năng liên cung của WS08, Hyper-V hỗ trợ cho việc khôi phục sau thảm hoạ trong môi trường IT và xuyên suốt các trung tâm dữ liệu dùng các tính năng liên cung phân tán theo địa lý. Tính năng khôi phục hoạt động và phục hồi sau thảm hoạ tin cậy và nhanh giúp đảm bảo việc mất mát dữ liệu tối thiểu.
Thử nghiệm và phát triển
Thử nghiệm và phát triển là những chức năng nghiệp vụ thường cần đến công nghệ ảo hoá. Dùng máy ảo, bộ phận phát triển có thể tạo và thử nghiệm với nhiều tình huống trong môi trường tách biệt và an toàn, mô phỏng chính xác hoạt động của server thực. Hyper-V cho phép khai thác tối đa phần cứng dùng cho thử nghiệm, giảm chi phí và cải thiện tầm thử nghiệm. Với các tính năng kiểm soát và hỗ trợ HĐH khách dồi dào, Hyper-V cung cấp một nền tảng tuyệt vời cho môi trường phát triển và thử nghiệm.
Trung tâm dữ liệu động
Hyper-V cùng với các giải pháp quản lý hiện hữu, như Microsoft System Center, giúp hiện thực tầm nhìn trung tâm dữ liệu động với khả năng cung cấp những hệ thống tự quản lý và làm việc linh hoạt. Với các tính năng như cấu hình máy ảo tự động, kiểm soát tài nguyên linh hoạt và “di cư” nhanh, DN có thể tạo một môi trường IT động sử dụng ảo hóa không chỉ để đối phó các sự cố, mà còn để lường trước các yêu cầu gia tăng.
Xuất hiện
Microsoft đã đưa ra bản tiền beta của thành phần ảo hóa (lúc đó còn mang tên Windows Server Virtualization) cùng với WS08 RC0 Enterprise 64-bit từ tháng 9/2007. Theo kế hoạch, bản beta của thành phần ảo hóa này có mặt khi WS08 ra mắt chính thức vào cuối tháng 2/2008, sau đó 180 ngày sẽ có phiên bản chính thức.
Tuy nhiên vào trung tuần tháng 12, Microsoft đã gây ngạc nhiên cho khách hàng và đối tác với việc đưa ra bản Hyper-V beta cùng với WS08 RC1 Enterprise (cho tải về tại địa chỉ http://www.microsoft.com/windowsserver2008/audsel.mspx), sớm hơn kế hoạch.
Khác với bản tiền beta, bản Hyper-V beta trong WS08 RC1 được cài đặt giống như các role khác, không còn các file .msu nữa (xem bài thử nghiệm trên TGVT A tháng 11, ID: A0711_88). Hyper-V beta chỉ hỗ trợ 2 HĐH khách: Windows Server 2003 và Windows Server 2008. Theo Microsoft, trong phiên bản chính thức Hyper-V sẽ hỗ trợ nhiều HĐH khách hơn (cả 32-bit và 64-bit).
Hyper-V sẽ có mặt trong 3 phiên bản WS08 64-bit (WS08 có tất cả 8 phiên bản): Standard (1 thực thể ảo), Enterprise (4 thực thể ảo) và Datacenter (không giới hạn thực thể ảo).
Ngoài ra, Microsoft còn cung cấp sản phẩm ảo hóa máy chủ độc lập có tên gọi Microsoft Hyper-V Server, chương trình bổ trợ Server Virtualization Validation Program cho phép các hãng cung cấp phần mềm máy ảo kiểm tra tính tương thích giải pháp của mình với các HĐH Windows Server.
Nguyễn Lê - pcworldvn
Nguồn: Microsoft
-----------------------------------------
Công nghệ ảo hóa
Hỏi (H). Công nghệ máy ảo là gì?
Đáp (Đ). Công nghệ máy ảo áp dụng cho cả phần cứng máy chủ và máy trạm. Công nghệ máy ảo cho phép nhiều hệ điều hành chạy đồng thời trên một máy tính duy nhất. Đặc biệt, Hyper V - một đặc tính then chốt của Windows Server 2008, còn cho phép hơn một hệ điều hành đồng thời chạy trên cùng một hệ thống vật lý. Ngày nay, nhiều hệ điều hành hoạt động trên nền kiến trúc x86 được hỗ trợ Virtual PC 2007, Virtual Server 2005, và Hyper-V.
H. Công nghệ máy ảo được dùng để làm gì?
Đ. Công nghệ máy ảo phục vụ cho nhiều mục đích phong phú. Công nghệ này cho phép hợp nhất phần cứng bởi vì nhiều hệ điều hành có thể cùng chạy trên một máy tính. Những ứng dụng then chốt của công nghệ máy ảo bao gồm khả năng tích hợp chéo giữa các nền tảng và các khả năng dưới đây:
- Hợp nhất máy chủ. Nếu nhiều máy chủ vận hành ứng dụng mà chỉ tiêu thụ một phần nhỏ tài nguyên sẵn có, thì công nghệ máy ảo có thể được sử dụng để cho phép nhiều ứng dụng chạy song song trên một máy chủ duy nhất, ngay cả khi các ứng dụng này cần tới những phiên bản hệ điều hành hay middleware khác nhau.
- Hợp nhất cho các môi trường triển khai và thử nghiệm. Mỗi máy ảo đóng vai trò như một môi trường riêng, điều này sẽ giảm bớt rủi ro và tạo điều kiện để các chuyên gia phát triển nhanh chóng tái xây dựng các cấu hình hệ điều hành khác nhau hoặc so sánh các phiên bản ứng dụng được thiết kế cho các hệ điều hành khác nhau. Ngoài ra, chuyên gia phát triển cũng có thể kiểm tra các phiên bản phát triển sớm của một ứng dụng trong một máy ảo mà không sợ làm mất đi tính ổn định của hệ thống đối với những người dùng khác.
- Re-hosting ứng dụng riêng. Các hệ điều hành và ứng dụng riêng có thể chạy trên phần cứng mới cùng với những hệ điều hành và ứng dụng được đưa ra gần đây hơn.
- Đơn giản hóa kế hoạch đối phó và khôi phục thảm họa. Công nghệ máy ảo có thể được sử dụng như một phần của kế hoạch phòng chống và khôi phục sau thảm họa. Kế hoạch như vậy thường yêu cầu ứng dụng phải có khả năng di động, linh hoạt trên khắp các nền tảng phần cứng.
- Chuyển tới một trung tâm dữ liệu động. Giờ đây, Hyper- V, cùng với những giải pháp quản lý hệ thống, giúp bạn tạo ra một môi trường CNTT năng động. Môi trường này không chỉ cho phép bạn phản ứng lại các sự cố một cách hiệu quả hơn mà còn xây dựng một giải pháp quản lý CNTT có khả năng tự quản lý và có tính chất phòng trừ.
H. Chiến lược ảo hóa của Microsoft là gì?
Đ. Mục tiêu của chúng tôi là giúp khách hàng biến các hệ thống CNTT của họ thành các hệ thống có khả năng tự quản lý và năng động để có thể kiểm soát tốt hơn các hệ thống CNTT của mình và để doanh nghiệp của họ đáp ứng nhanh hơn và luôn ở thế tiên phong trong cuộc cạnh tranh. Để làm được điều đó, chúng tôi:
- Đem tới một bộ toàn diện các sản phẩm ảo hóa mà có thể mở rộng từ desktop tới một trung tâm dữ liệu.
- Giúp quản lý tất cả tài sản CNTT – cả tài sản vật lý lẫn tài sản ảo – từ một nền tảng duy nhất.
Microsoft đang đầu tư lớn vào các lĩnh vực như nền tảng, quản lý, ứng dụng, khả năng kết hợp uyển chuyển các sản phẩm/ giải pháp từ những nhà cung cấp khác nhau, và cấp phép. Đồng thời, chúng tôi đang nỗ lực tạo điều kiện để người dùng tận dụng được các lợi thế từ khoản đầu tư hiện tại của mình cho nền tảng, sử dụng những kỹ năng và cơ sở hạ tầng hỗ trợ hiện có, và giảm bớt chi phí gắn với việc triển khai các môi trường ảo hóa.
Hyper-V—Tổng quan
 Hỏi (H). Hyper-V là gì?
Đáp (Đ).
Hỏi (H). Hyper-V là gì?
Đáp (Đ). Hyper-V, tên mã trước đây là Viridian, là một công nghệ dựa trên hypervisor và là một đặc tính then chốt của Windows Server 2008. Công nghệ này đem tới một nền tảng ảo hóa có khả năng mở rộng, tin cậy và tính sẵn sàng cao. Đó là một phần trong nỗ lực liên tục của Microsoft nhằm cung cấp cho khách hàng và đối tác của chúng tôi một nền tảng hệ điều hành tốt nhất cho ảo hóa.
H. Windows hypervisor là gì?
Đ. Là thành phần lõi của Hyper-V, Windows hypervisor là một lớp phần mềm mỏng giữa phần cứng và hệ điều hành để cho phép chạy nhiều hệ điều hành mà không phải chỉnh sửa trên một máy chủ tại cùng thời điểm. Thành phần này cung cấp chức năng phân vùng đơn giản và chịu trách nhiệm duy trì sự tách biệt rõ rệt giữa các phân vùng. Windows hypervisor kế thừa một kiến trúc bảo mật với bề mặt tấn công tối thiểu vì không chứa bất cứ trình điều khiển thiết bị nào của hãng thứ ba
H. Hyper-V mang lại lợi ích gì cho khách hàng?
Đ. Hyper-V cung cấp cho khách hàng một nền tảng lý tưởng trong các tình huống ảo hóa cơ bản, như củng cố máy chủ sản xuất, quản lý sự liên tục của hoạt động kinh doanh, chạy thử và phát triển phần mềm, và xây dựng trung tâm dữ liệu động.
Hyper-V cung cấp chức năng cơ bản mà một nền tảng ảo hóa lý tưởng cần có – khả năng mở rộng, hiệu năng cao, tính tin cậy, bảo mật linh hoạt, và khả năng quản lý. Hyper-V mang lại khả năng mở rộng và hiệu năng cao qua việc hỗ trợ các tính năng như hỗ trợ đa xử lý máy trạm và hỗ trợ máy chủ và khách trên nền tảng 64-bit, tính tin cậy và bảo mật thông qua kiến trúc hypervisor; tính linh hoạt và khả năng quản lý qua việc hỗ trợ các tính năng như chuyển nhanh các máy ảo từ một máy chủ vật lý đến một máy khác, và tích hợp với System Center Virtual Machine Manager.
Đ. Liệu Microsoft sẽ tiếp tục hỗ trợ các hệ điều hành Linux với Hyper-V không?
H. Có. Microsoft sẽ cung cấp các thành phần tích hợp và hỗ trợ kỹ thuật cho khách hàng sử dụng các phiên bản Linux với tư cách là các hệ điều hành khách trong Hyper-V. Các thành phần tích hợp Linux bản beta hiện đang có sẵn đối với SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 SP1 các phiên bản x86 và x64. Các thành phần tích hợp này cho phép hệ điều hành Linux có Xen tận dụng kiến trúc VSP/VSC và mang lại hiệu năng cao hơn. Các thành phần tích hợp Linux bản beta hiện có sẵn để download ngay tại địa chỉ:
http://connect.microsoft.com.
H. Các phiên bản Linux khác thì sao?
Đ. Danh sách đầy đủ các hệ điều hành hỗ trợ sẽ được thông báo trước khi công bố bản RTM.
H. Công ty có thể giới thiệu khái quát về bộ tính năng của Hyper-V được không?
Đ. Một trong số những khả năng của Hyper-V là hỗ trợ máy chủ và khách trên nền x64, khả năng chạy máy trạm trong một môi trường đa xử lý, phân phối bộ nhớ lớn cho mỗi máy ảo, hỗ trợ chuyển đổi ảo tích hợp, và khả năng dịch chuyển lên các máy ảo trên khắp máy chủ với thời gian tạm dừng hoạt động ngắn nhất. Các đặc tính mới, then chốt của Hyper-V bản beta là hỗ trợ dịch chuyển nhanh và tính sẵn có cao, khả năng chạy Hyper-V với vai trò Server Core và tích hợp Hyper-V vào Server Manager. Để xem danh sách đầy đủ các chức năng, tham khảo
mục các đặc tính then chốt trong Hyper-V RC.
H. Khách hàng sẽ chuyển sang Hyper-V như thế nào?
Đ. Các khách hàng đầu tư vào định dạng file .vhd—định dạng được sử dụng bởi Virtual Server, cũng như nhiều hãng được cấp phép bán sản phẩm—sẽ có một hướng đi thông suốt tới Hyper-V. Khách hàng có thể tạo đòn bẩy cho các tính năng V2V trong System Center Virtual Machine Manager để chuyển đổi một cách thuận tiện từ Virtual Server hoặc VMware sang Hyper-V hoặc làm việc với các đối tác của Microsoft cung cấp các giải pháp chuyển đổi. .
Hỏi (H). Phiên bản Hyper-V nào đi kèm với Windows Server 2008??
Đáp (Đ). Một phiên bản RC của Hyper-V hiện đang có sẵn với Windows Server 2008 RTM x64. Trước đây, một phiên bản preview công nghệ dành cho khách hàng (CTP) của Hyper-V đã được cung cấp như là một phần của các phiên bản 64-bit của Windows Server 2008 Release Candidate 0 (RC0).
H. Làm thế nào người sử dụng truy cập được Hyper-V RC?
Đ. Người sử dụng có thể download và cài đặt bản cập nhật cho RC từ đây hoặc thông qua Windows Update. Người sử dụng có thể vào Server Manager và cài đặt chức năng Hyper-V. Sau khi chức năng Hyper-V được bật, trình quản lý Hyper-V sẽ có mặt trong Administrative Tools. Từ trình Hyper-V Manager, người sử dụng có thể dễ dàng tạo và cấu hình các máy ảo.
H. Ai nên tham gia vào bản beta? Bản beta dành cho tất cả mọi người hay không?
Đ. Microsoft khuyến khích tất cả khách hàng và đối tác thử nghiệm và đánh giá bản beta của Hyper-V. Hướng dẫn cài đặt chi tiết có ở trang Cài đặt Hyper-V của Windows Server như thế nào.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cài đặt xem tại trang
Cài đặt Hyper-V của Windows Server như thế nào.
H. Sự khác biệt cơ bản giữa bản RC và Beta của Hyper-V là gì?
Đ. Bản RC của Hyper-V hiện dành cho các phiên bản Windows Server 2008 x64. Khách hàng được khuyến khích sử dụng bản này để đánh giá và thử nghiệm Hyper-V. Với bản RC, Hyper-V hiện giờ có đầy đủ tính năng và đem tới một hướng đi uyển chuyển để nâng cấp lên bản RTM của Hyper-V. Những cập nhật mới, then chốt trong Hyper-V RC là nâng cao tính ổn định và khả dụng, bao gồm bản địa hóa một phần cho tiếng Đức và tiếng Nhật, hỗ trợ thêm Hệ điều hành khách và cải thiện hiệu năng. Để xem danh sách đầy đủ các tính năng, xin tham khảo các đặc tính then chốt trong Hyper-V RC.
H. Tính năng của bản RC này có hoàn thiện không? Công ty có dự định thêm hay bớt tính năng gì không ?
Đ. Bản Hyper-V RC đã hoàn thiện về mặt tính năng, và được thiết kế để thử nghiệm và đánh giá cho các tính huồng triển khai cuối cùng. Điều này tạo cơ hội để Microsoft có được những phản hồi quý báu từ khách hàng và đối tác.
H. Mục tiêu của bản RC này là gì?
Đ. Mục tiêu của bản RC này là cung cấp cho khách hàng và đối tác một phiên bản Hyper-V đầy đủ tính năng để đánh giá và bắt đầu lên kế hoạch, thử nghiệm và phản hồi cho Microsoft.
H. Những người thử nghiệm sẽ thấy gì khi họ download Hyper-V?
Đ. Khách hàng download các phiên bản Windows Server 2008 x64, và họ sẽ phải bật chức năng ảo hóa thông qua Server Manager. Bản cập nhật cho phiên bản RC có sẵn nhờ download riêng hoặc qua Windows Update. Sau khi chức năng Hyper-V được bật, trình quản lý Hyper-V Manager sẽ thành một phần trong Administrative Tools. Từ trình Hyper-V Manager, người sử dụng có thể dễ dàng tạo ra và cấu hình các máy ảo
H. Microsoft có cung cấp hỗ trợ kỹ thuật cho những người tham gia bản RC không?
Đ. Không có hỗ trợ kỹ thuật trực tiếp. Chúng tôi chỉ hỗ trợ dưới hình thức thông tin nhóm.
H. Hướng dẫn sử dụng/triển khai Hyper-V RC?
Đ. Chỉ nên sử dụng Hyper-V RC cho mục đích đánh giá và thử nghiệm. Việc triển khai sản xuất bản RC sẽ không được hỗ trợ.
H. Hiệu năng mong đợi của Hyper-V RC là gì? So với Virtual Server như thế nào? So với ESX server như thế nào?
Đ. Chúng ta sẽ thực hiện hầu hết các nhiệm vụ liên quan đến hiệu năng giữa bản beta và RTM của Hyper-V. Tại thời điểm này, chúng ta hài lòng với những tiến bộ đạt được về mặt hiệu năng giữa bản Beta và RC. Chúng tôi sẽ không công bố số liệu về hiệu năng vào thời điểm này.
H. Tôi có thể nâng cấp Hyper-V Beta lên Hyper-V RC được không?
Đ. Các khách hàng có thể nâng cấp các hệ thống Hyper-V Beta hiện tại chạy Windows Server 2008 RTM qua dịch vụ Windows Update. Khuyến cáo các khách hàng nên sao lưu VHD trước khi cài đặt các bản cập nhật. Khách hàng sẽ cần phải tạo lại các chế độ cài đặt máy ảo và switch ảo trên máy chủ nhưng có thể sử dụng lại các VHD sẵn có của mình. Xem hướng dẫn chi tiết chuyển đổi Hyper V.
H. Danh sách của những máy trạm sẽ được hỗ trợ trên Hyper-V là gì? Khi nào chúng tôi có thể mong chờ hỗ trợ cho những hệ điều hành như Windows Vista, Windows XP, Linux, v.v…?
Đ. Nói chung, Microsoft không hỗ trợ những bản phần mềm được đưa ra trước khi phát hành chính thức bao gồm CTP, beta, và bản RC. Tuy nhiên, các diễn đàn trực tuyến và nhóm tin tức thì có. Những hệ điều hành máy trạm đã được thử nghiệm trên bản RC Hyper-V là: các bản Windows Server 2003,các bản Windows Server 2008, các bản Windows Vista SP1 x86, Windows XP SP3 x86, và SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 Service Pack 1. Trên thực tế, các thành phần tích hợp Linux bản beta hiện đã có cho Bản SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 SP1 x86 và x64 . Các thành phần tích hợp Linux bao gồm hỗ trợ cho cả trình tiếp hợp mạng tổng hợp và trình điều khiển lưu trữ tổng hợp. Các thành phần tích hợp cũng bao gồm Hypercall Adapter. Hypercall Adapter là một lớp phần mềm mỏng nằm dưới nhân Linux có Xen và dịch các call ảo hóa cụ thể cho Xen đến hypercall của Microsoft Hyper-V mang lại hiệu năng cao hơn. Các thành phần tích hợp Linux beta có thể download ngay tại
http://www.connect.microsoft.com.
Để xem toàn bộ danh sách các hệ điều hành hỗ trợ cho Hyper-V RTM, xin tham khảo tại:
http://www.microsoft.com/windowsserver2008/en/us/hyperv-supported-guest-os.aspx.
H. Hệ điều hành khách nào được hỗ trợ với Hyper-V ở bản RC?
Đ. Nói chung, Microsoft không hỗ trợ những bản phần mềm được phát hành trước bao gồm CTP, beta, và bản RC. Tuy nhiên, có sẵn các diễn đàn trực tuyến và các nhóm tin tức hỗ trợ.Những hệ điều hành đã được thử nghiệm trên bản Hyper-V RC là:
Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2003, Vista, XP và SUSE 10 sẽ được hỗ trợ với Hyper-V.
- Windows Server 2008 x86 (VM cấu hình 1, 2 hoặc 4-way SMP)
- Windows Server 2008 x64 (VM cấu hình 1, 2 hoặc 4-way SMP)
- Windows Server 2003 x86 (VMs chỉ cấu hình 1 hoặc 2-way SMP)
- Windows Server 2003 x64 (VMs chỉ cấu hình 1-way)
- Windows Vista x86 Service Pack 1 (VMs chỉ cấu hình 1-way)
- Windows XP x86 Service Pack 3 (VMs chỉ cấu hình 1-way)
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 Service Pack 1 x86 Edition
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 Service Pack 1 x64 Edition
H. Điểm khác nhau giữa Hyper-V và Virtual Server là gì?
Đ. Microsoft Virtual Server 2005 R2 là giải pháp ảo hóa cho máy chủ hiện tại của Microsoft và được dựa trên nền tảng ảo hóa trên máy chủ. Hyper-V, một tính năng chính của Windows Server 2008, là một nền tảng ảo hóa dựa trên hypervisor sẽ giúp cho người dùng không chỉ hợp nhất một mảng rộng lớn khối lượng công việc mà còn cho phép chuyển hướng đến một môi trường CNTT năng động. Đặc tính cốt lõi tạo ra sự khác biệt bao gồm khả năng hỗ trợ 64 máy trạm ảo, hỗ trợ SMP, cải thiện hiệu năng và nhiều tính năng quan trọng khác trong Hyper-V.
H. Liệu sẽ có phiên bản Hyper-V nào được bản địa hóa không?
Đ. Hyper-V RC hiện đã có bản tiếng Anh và các bản được bản địa hóa một phần cho tiếng Đức và tiếng Nhật. Chúng tôi chưa thông báo về kế hoạch bản địa hóa cho Hyper-V.
---------------------------------------------------------
Basics of Licensing for Virtual Environments
Click the animation above to learn how Microsoft licensing supports virtualization scenarios. Then, explore how licensing works for the four elements of virtualization: server, desktop, application, and management.
Follow the product links below for more virtualization information.
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise: Run up to four software instances at a time in virtual operating system environments on a server under a single server license.
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter: Run any number of software instances in physical and virtual operating system environments on a server.
- Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Enterprise: Run any number of software instances in one physical server and any number of virtual operating system environments on the server.
- Windows Virtual Desktop Access (Windows VDA): A standard benefit of Software Assurance and a stand-alone subscription-based license which allows roaming access to Windows virtual machines (VMs) from thin clients, third party, and non-Windows-based devices.
- System Center Server Management Suite Enterprise (SMSE): SMSE offers a comprehensive solution that includes Virtual Machine Manager and covers the managed node under the four main products of System Center. One SMSE license allows you to manage the physical operating system environment and up to four virtual ones on a licensed server.
- Microsoft Desktop Optimization Pack (MDOP) for Software Assurance: MDOP offers a suite of technologies that can help reduce application management costs, instantly deliver virtualized applications, and better control desktop environments, enhancing IT responsiveness and user uptime.
- Enrollment for Core Infrastructure: The Enrollment for Core Infrastructure helps you easily acquire the foundation for a more protected, well-managed IT infrastructure by offering a cost-efficient way to license software together in a simple per processor license.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------

Overview of Hyper-V
Applies To: Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2
Hyper-V in Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 enables you to create a virtualized server computing environment. You can use a virtualized computing environment to improve the efficiency of your computing resources by utilizing more of your hardware resources. This is possible because you use Hyper-V to create and manage virtual machines and their resources. Each virtual machine is a virtualized computer system that operates in an isolated execution environment. This allows you to run multiple operating systems simultaneously on one physical computer.
 Note Note |
|---|
Hyper-V is a hypervisor-based virtualization technology that requires specific hardware. For more information about the requirements and other considerations, see the following:
|
What does Hyper-V do ?
Hyper-V provides software infrastructure and basic management tools that you can use to create and manage a virtualized server computing environment. This virtualized environment can be used to address a variety of business goals aimed at improving efficiency and reducing costs. For example, a virtualized server environment can help you:
- Reduce the costs of operating and maintaining physical servers by increasing your hardware utilization. You can reduce the amount of hardware needed to run your server workloads.
- Increase development and test efficiency by reducing the amount of time it takes to set up hardware and software and reproduce test environments.
- Improve server availability without using as many physical computers as you would need in a failover configuration that uses only physical computers.
Who will be interested in this role?
Hyper-V can be useful to you if you are:
- An IT administrator, planner, or designer.
- An IT architect responsible for computer management and security throughout your organization.
- An IT operations manager who is looking for ways to reduce the total cost of ownership of their server infrastructure, in terms of both power costs and management costs.
- A software developer or tester who is looking for ways to increase productivity by reducing the time it takes to build and configure a server for development or test use.
What are the key features of Hyper-V?
The key features of Hyper-V are as follows:
- 64-bit native hypervisor-based virtualization.
- Ability to run 32-bit and 64-bit virtual machines concurrently.
- Uniprocessor and multiprocessor virtual machines.
- Virtual machine snapshots, which capture the state, data, and hardware configuration of a running virtual machine. Because snapshots record system states, you can revert the virtual machine to a previous state.
- Large virtual machine memory support.
- Virtual local area network (VLAN) support.
- Microsoft Management Console (MMC) management snap-in.
- Documented Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) interfaces for scripting and management.
Hyper-V in Windows Server 2008 R2 adds the following features:
- Live migration
- Dynamic virtual machine storage
- Enhanced processor support
- Enhanced networking support
For more information about the new Hyper-V features included in Windows Server 2008 R2, see
What's New in Hyper-V in Windows Server 2008 R2. For more information about the WMI interfaces, see Virtualization WMI Provider (
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=108564).
In This Collection
The following table lists the documents within each section of the Hyper-V collection and provides other related resources.
Related Resources
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Microsoft Hyper-V
Microsoft
Hyper-V, codenamed
Viridian[5] and formerly known as
Windows Server Virtualization, is a
hypervisor-based
virtualization system for
x86-64 systems.
[6] A beta version of Hyper-V was shipped with certain x86-64 editions of
Windows Server 2008, and the finalized version (automatically updated through
Windows Update) was released on June 26, 2008.
[7] Hyper-V has since been released in a free stand-alone version, and has been upgraded to Release 2 (R2) status.
[citation needed]
Versions and variants
Hyper-V exists in two variants: as a stand-alone product called Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2008, and as an installable role in
Windows Server 2008 R2 and
Windows Server 2008 (the former containing the later release of Hyper-V).
The stand-alone version of Hyper-V is free, and was released on October 1, 2008. It is a variant of the core installation of
Windows Server 2008 that includes full Hyper-V functionality; other Windows Server 2008 roles are disabled, and there are limited Windows Services.
[8] The free Hyper-V Server 2008 variant is limited to a command line interface (CLI), where configuration of the "Host" or "Parent" (Hyper-V Server 2008) OS, physical hardware and software is done using shell commands. A new menu driven CLI interface does simplify initial configuration considerably, and some freely downloadable script files extend this concept. Administration and configuration of the "Host" (Hyper-V Server 2008 OS) and the "guest" or virtual OSes is generally done by downloading extended
Microsoft Management Consoles that are installed onto a Windows 7 PC or Windows 2008 Server (32 or 64 bit) or System Center Virtual Machine.
Alternatively, another Windows Server 2008 computer, with the Hyper-V role installed, can be used to manage Hyper-V Server 2008 by redirecting the management console. Other administration and configuration of Hyper-V Server 2008 can be done using a
Remote Desktop RDP session (though still CLI) or redirected standard management consoles (MMC) such as "Computer Management" and "Group Policy (Local)" from a Vista PC or a full installation of Windows 2008 Server. This allows much easier "point and click" configuration, and monitoring of the Hyper-V Server 2008. Hyper-V Server Release 2 (R2) was made available in September 2009, its main feature being the inclusion of
Windows Powershell v2 for greater CLI control, and the updated Windows Server 2008 R2 code base.
Architecture
Hyper-V supports isolation in terms of a
partition. A partition is a logical unit of isolation, supported by the hypervisor, in which
operating systems execute. A hypervisor instance has to have at least one
parent partition, running
Windows Server 2008. The virtualization stack runs in the parent partition and has direct access to the hardware devices. The parent partition then creates the
child partitions which host the guest OSs. A parent partition creates child partitions using the
hypercall API, which is the
application programming interface exposed by Hyper-V.
[9]
A virtualized partition does not have access to the physical
processor, nor does it handle its real
interrupts. Instead, it has a virtual view of the processor and runs in
Guest Virtual Address, which, depending on the configuration of the hypervisor, might not necessarily be the entire
virtual address space. A hypervisor could choose to expose only a subset of the processors to each partition. The hypervisor handles the interrupts to the processor, and redirects them to the respective partition using a logical
Synthetic Interrupt Controller (SynIC). Hyper-V can hardware accelerate the address translation of Guest Virtual Address-spaces by using second level address translation provided by the CPU, referred to as EPT on Intel and NPT on AMD.
Child partitions do not have direct access to hardware resources, but instead have a virtual view of the resources, in terms of
virtual devices. Any request to the virtual devices is redirected via the
VMBus to the devices in the parent partition, which will manage the requests. The VMBus is a logical channel which enables inter-partition communication. The response is also redirected via the VMBus. If the devices in the parent partition are also virtual devices, it will be redirected further until it reaches the parent partition, where it will gain access to the physical devices. Parent partitions run a
Virtualization Service Provider (VSP), which connects to the VMBus and handles device access requests from child partitions. Child partition virtual devices internally run a
Virtualization Service Client (VSC), which redirect the request to VSPs in the parent partition via the VMBus. This entire process is transparent to the guest OS.
Virtual Devices can also take advantage of a Windows Server Virtualization feature, named
Enlightened I/O, for storage, networking and graphics subsystems, among others. Enlightened I/O is specialized virtualization-aware implementation of high level communication protocols like
SCSI to take advantage of VMBus directly, that allows bypassing any device emulation layer. This makes the communication more efficient, but requires the guest OS to support Enlightened I/O.
Windows Server 2008,
Windows Vista,
Red Hat Enterprise Linux, and
SUSE Linux are currently the only operating systems that support Enlightened I/O, allowing them therefore to run faster as guest operating systems under Hyper-V than other operating systems that need to use slower emulated hardware.
System requirements / specifications
- Host operating system:
- To install the Hyper-V role, Windows Server 2008 (64-bit only) or 2008 R2 Standard, Enterprise or Datacenter edition is required. Installation on the Web and/or Foundation editions is not possible; neither is it possible on 32-bit (x86-32) versions of Windows Server 2008 nor IA64 editions.
- It can be installed regardless of whether the installation is a full or core installation.
- Processor:
- An x86-64 processor
- Hardware-assisted virtualization. This is available in processors that include a virtualization option; specifically, Intel VT or AMD Virtualization (AMD-V, formerly code-named "Pacifica").
- A NX bit-compatible CPU must be available and Hardware Data Execution Prevention (DEP) must be enabled.
- Although this is not an official requirement, Windows Server 2008 R2 and a CPU with Extended Page Table support are recommended for workstations.[10]
- Memory
- Minimum 2 GB. (Each virtual OS requires its own memory, and so realistically much more.)
- Windows Server 2008 Standard (x64) Hyper-V full GUI or Core supports up to 31 GB of memory for running VMs, plus 1 GB for Hyper-V parent OS.[11]
- Maximum total memory per system for Windows Server 2008 R2 hosts: 32 GB (Standard) or 2 TB (Enterprise, Datacenter) [12]
- Guest operating systems
- Hyper-V supports virtual machines with up to 4 processors each (1, 2, or 4 processors depending on guest OS-see below )
- Hyper-V supports up to 384 VMs per system[13]
- Hyper-V supports both 32-bit (x86) and 64-bit (x64) guest VMs.
Microsoft Hyper-V Server
The stand-alone Hyper-V Server variant does not require an existing installation of Windows Server 2008 nor Windows Server 2008 R2. The standalone installation is called Microsoft Hyper-V Server for the non-R2 version and Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2008 R2. Microsoft Hyper-V server is built with components of Windows and has a Windows Server Core user experience. None of the other roles of Windows Server are available in Microsoft Hyper-V Server. This version supports up to 64 VMs per system.
[14]System requirements of Microsoft Hyper-V server are the same for supported guest operating systems and processor, but differ in the following :
[15]
- RAM: Minimum: 1 GB RAM; Recommended: 2 GB RAM or greater; Maximum 1 TB.
- Available disk space: Minimum: 8 GB; Recommended: 20 GB or greater.
Supported guests
The following is a table of supported guest operating systems.
[16] Other guest operating systems such as
Ubuntu Linux 6.06/6.10/7.10 or
Fedora 8/9 are unsupported; however, they have been reported to run.
[17][18][19] [16]
| Guest OS | Virtual processors | Edition(s) |
|---|
| Windows 7 | 1,2 or 4 | Both x86-32 and x86-64, all editions except home editions (the home editions are Home Premium, Home Basic, and Starter) |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 1,2 or 4 | x64, Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter |
| Windows Server 2008 | 1,2 or 4 | Both x86 and x64, Web, HPC, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, with or without Hyper-V |
| Linux (only including SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 with SP3 or version 11 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux versions 5.2-6.1), CentOS 5-2-6.0 | 1,2 or 4 | Both x86 and x64 |
| Windows Server 2003 | 1 or 2 | Both x86 and x64, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, SP2 required |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 | 1 or 2 | Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, both x86 and x64 except for Web whose 64-bit version is not supported |
| Windows 2000 Server | 1 | Server, Advanced Server, SP4 required |
| Windows Vista | 1 or 2 | Both x86 and x64, all editions except home editions |
| Windows XP | 1 or 2 | x86, Professional edition only, SP3 required |
| Windows XP x64 Edition | 1 or 2 | x64, Professional edition only, SP2 required |
| Windows Small Business Server 2011 | 1, 2 or 4 | Essentials, Standard (Essentials supports only 2 virtual CPUs) |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | 1, 2 or 4 | Standard |
| Windows Storage Server 2008 R2 Essentials | 1, 2 or 4 | Essentials |
| Others | 1 | N/A |
Desktop virtualization (
VDI) products are available from third-party companies,
Quest Software vWorkspace,
Citrix XenDesktop,
Systancia AppliDis Fusion
[20] and
Ericom PowerTerm WebConnect, that provide the ability to host and centrally manage desktop virtual machines in the data center while giving end users a full PC desktop experience.
Guest operating systems with
Enlightened I/O and a
hypervisor-aware kernel such as
Windows Server 2008 and later server versions,
Windows Vista SP1 and later clients and offerings from Citrix XenServer and Novell will be able to use the host resources better since VSC drivers in these guests communicate with the VSPs directly over VMBus.
[21] Non-enlightened operating systems will run with emulated I/O;
[22] however,
integration components (which include the VSC drivers) are available for
Windows Server 2003 SP2, Windows Vista SP1 and Linux to achieve better performance.
Xen-enabled Linux guest distributions can also be
paravirtualized in Hyper-V. Currently, only
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 SP1/SP2 x86 and x64 Editions are officially supported by Microsoft in this way,
[23] though any Xen-enabled Linux should be able to run. In February 2008,
Red Hat and Microsoft signed a virtualization pact for hypervisor interoperability with their respective server operating systems, to enable
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 to be officially supported on Hyper-V.
[24]
Linux support
In July 2009 Microsoft submitted Hyper-V drivers to the kernel, which improve the performance of virtual
Linux guest systems in a Windows hosted environment. Microsoft was forced to submit the code when it was discovered that Microsoft had incorporated a Hyper-V network driver with GPL-licensed components statically linked to closed-source binaries. Hyper-V provides basic virtualization support for Linux guests out of the box.
Paravirtualization support is, however, available by installing the
Linux Integration Components
or
Satori InputVSC
drivers. On July 20, 2009, Microsoft submitted these drivers for inclusion in the
Linux kernel under the terms of the
GPL,
[25]so that kernels from 2.6.32 may include inbuilt Hyper-V paravirtualization support.
VHD compatibility with Virtual Server 2005 and Virtual PC 2004/2007
Hyper-V, like Virtual Server 2005 and Virtual PC 2004/2007, saves each guest OS to a single virtual hard disk file with the extension
.VHD. This file contains the entire guest OS, though other files can also be configured to allow "undo information" etc.
Older .vhd files from Virtual Server 2005 and Virtual PC 2004/2007 can be copied and used by Windows 2008 Hyper-V Server, but the old "Virtual Machine add-ons" require removing prior to migration. After the migrated guest OS is configured and started using Hyper-V, the guest OS will detect changes to the (virtual) hardware. Installing "Hyper-V Integration Services" installs five services to improve performance, at the same time adding the new Guest Video and Network Card drivers. Consequently later versions of Windows may require re-activation. Virtual Server 2005 R2 SP1 supports guest operating systems OS/2 4.5 and Solaris 10 while Hyper-V does not.
Limitations
USB passthrough
Hyper-V does not support virtualized USB ports or COM ports.
[26] [27] However, a workaround to access USB drives in Windows guest VMs involves using the Microsoft Remote Desktop Client to "share" host drives with guests over a
Remote Desktop Connection.
Other techniques exist to allow USB utilisation, an example would be using a network to USB device and extracting the "usbd.sys" file from the installation media to the host machine.
Audio
Audio hardware is not virtualized by Hyper-V although the above Remote Desktop workaround may be used.
Optical drives pass-through
Optical drives virtualized in the guest VM are read-only.
[28] Hyper-V does not support the host/root operating system's optical drives to pass-through in guest VMs. As a result, burning to discs, audio CDs, video CD/DVD-Video playback are not supported.
Graphics issues on the host
When manufacturer-supplied Vista-compatible
(WDDM) display drivers are installed on the host OS, most servers and PCs will experience a dramatic drop in graphic performance, including 'page flipping'-like effects when viewing high definition content or scrolling in applications and system hangs when switching between applications on the host; guest systems performance is unaffected. Users may install XP/2003-compatible (Non-WDDM) display drivers but may have compatibility problems and will be unable to use
Aero. This occurs regardless of whether a VM actually exists or whether any Hyper-V services are running.
[29]
Microsoft recommends to use default VGA drivers (shipped with Windows Server 2008) on the host systems instead of manufacturer- supplied ones,
[30] however, such drivers, in turn, do not support multiple displays and high resolution configurations, as well as Aero,
DirectX,
Hardware-accelerated video decoding and other graphic accelerated features, thereby limiting its use on workstations (default VGA drivers do not support e.g. resolutions higher than 1280x1024).
This issue in Windows Server 2008 (not R2) is still not solved. According to a Microsoft specialist's statement, systems with Windows Server 2008 R2 and processors supporting
Extended Page Table are unaffected;
[10] however, at least some users experience an even more significant problem: Windows Server 2008 R2 with Hyper-V and manufacturer-supplied graphic drivers installed won't boot at all.
[31] This issue is fixed in Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1.
[citation needed]
Live migration
Hyper-V in Windows Server 2008 (not R2) does not support "live migration" of guest VMs (where "live migration" is defined as maintaining network connections and uninterrupted services during VM migration between physical hosts). Instead, Hyper-V on Server 2008 Enterprise and Datacenter Editions supports "quick migration", where a guest VM is suspended on one host and resumed on another host. This operation happens in the time it takes to transfer the active memory of the guest VM over the network from the first host to the second host.
[32]
However, with the release of
Windows Server 2008 R2, Live Migration is supported with the use of
Cluster Shared Volumes (CSVs). This allows for failover of an individual VM as opposed to the entire host having to failover (it seems that when a node (Hyper-V server, not a VM) fails then each "VM running on the failed node" may migrate to other live nodes independently of "other VMs on the same LUN running on other nodes that share the LUN with the failed node". In Hyper-V we are clustering the Hyper-V nodes not the VMs.). See also
Cluster Shared Volumes
Degraded performance for Windows XP VMs
32-bit Windows XP guests running on Hyper-V experience degraded CPU and I/O performance because the Windows XP kernel frequently accesses the CPU APIC's
Task Priority Register (TPR) which Hyper-V intercepts putting more overhead on the hypervisor.
[33] While there is no resolution for this issue, some Intel CPUs include a technology called vTPR which works around this issue. AMD CPUs have a software workaround. 32-bit and 64-bit editions of Windows Server 2003, Windows XP x64 Edition and Windows Vista and later Windows versions are not affected.
NIC teaming
Network card teaming or
link aggregation is only supported if the NIC manufacturer supplied drivers support NIC teaming.
[34]
Future
The Developer Preview of
Windows 8 Server
[35] presented at the Microsoft Build Event
[36] contains the future version of Hyper-V. Some of the new features are listed below.
- Network virtualization[37]
- Extensible Hyper-V Virtual Switch
- Multi-tenancy
- NIC teaming as part of Windows Server 8 OS
- Up to 160 logical processors per physical server
- Up to 32 virtual processors per VM
- Storage Resource Pools
- .vhdx disk format supporting virtual hard disks as large as 16 TB with power failure resiliency
- Virtual Fibre Channel
- Offloaded data transfer
- Hyper-V replica
- Cross-premise connectivity
- Cloud backup
- VMs can now access up to 512GB of memory each
(The following have been released at Microsoft's BUILD conference in addition to the above.
[38])
- Each hypervisor instance can now access up to 2TB of memory.
- Up to 1024 total virtual processors per host
- Up to 1024 active VMs per host
- Up to 4000 active VMs per failover cluster
The version of Hyper-V shipped with the client version of Windows 8 requires a
SLAT-enabled processor, while Windows Server 8 only requires it if the
RemoteFX role is enabled.
[39]
See also
References
- ^ "Comprehensive List of Hyper-V Updates"
. Technet.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2010-03-02.
- ^ http://support.microsoft.com/kb/950050
- ^ http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff394763%28WS.10%29.aspx
- ^ http://support.microsoft.com/kb/976932
- ^ "Microsoft to ship Windows Server 2008, over time, in eight flavors"
. Retrieved 2007-11-13.
- ^ Paul Thurrott. "Windows Server Virtualization Preview"
. Retrieved 2007-09-25.
- ^ "http://www.microsoft.com/presspass/features/2008/jun08/06-26hyperv.mspx"
. Retrieved 2008-06-26.
- ^ Microsoft Helps Customers Overcome Barriers to Virtualization and Get Virtual Now
. . PressPass (Microsoft). October 1, 2008 2. Retrieved 2008-10-02.
- ^ "Benchmarking Hyper-V on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64"
. Retrieved 2010-01-28.
- ^ a b Virtual PC Guy's WebLog : Understanding High-End Video Performance Issues with Hyper-V
- ^ "Memory Limits for Windows Releases (Windows)"
. Msdn.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2010-03-02.
- ^ http://www.microsoft.com/windowsserver2008/en/us/system-requirements.aspx
- ^ "Microsoft Hyper-V Server: Overview"
. Microsoft.com. Retrieved 2010-03-02.
- ^ "Microsoft Hyper-V Server:Frequently asked questions"
.
- ^ "Microsoft Hyper-V Server: System Requirements"
. Microsoft.com. Retrieved 2010-03-16.
- ^ a b Supported Guest OS on Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V
- ^ Installing Fedora Core 8 on Hyper-V
- ^ First Look: Fedora 9 Alpha, Running in Hyper-V Beta: CRN
- ^ Install Ubuntu 7.10 on Hyper-V
- ^ "Systancia offers application and desktop virtualization in a single product"
. DataMonitor.
- ^ Hyper-V solution overview
- ^ Microsoft's Hyper-V: why all the fuss?
- ^ Microsoft Hyper-V To Flaunt Advanced Virtualization Features
- ^ Microsoft and Red Hat sign virtualization pact
- ^ "Microsoft Contributes Linux Drivers to Linux Community: Roundtable Q&A: Sam Ramji, senior director of Platform Strategy at Microsoft, and Tom Hanrahan, director of Microsoft’s Open Source Technology Center, discuss the company’s release of Linux device driver code under General Public License v2"
. Microsoft.com. 2009-07-20. Retrieved 2010-03-02.
- ^ Hyper-V FAQ
- ^ Known Issues with Running Windows Small Business Server 2008 in a Hyper-V Environment
- ^ DVD writer on Hyper-V server
- ^ Poor Host System Performance after RC1 Update (RTM as Well)
- ^ Video performance may decrease when a Windows Server 2008-based computer has the Hyper-V role enabled and an accelerated display adapter installed
- ^ Hyper-V install = Blue Screen - VIDEO_TDR_FAILURE
- ^ Hyper-V Live Migration vs. Quick Migration
- ^ Degraded I/O Performance using a Windows XP Virtual Machine with Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V
- ^ Microsoft Support Policy for NIC Teaming with Hyper-V
- ^ "Windows Server 8 (Video and Slides)"
.
- ^ "Microsoft Build Windows Server 8 and Hyper-V 3.0 sessions (Video and Slides)"
.
- ^ "A deep dive into Hyper-V Networking (Video and Slides)"
.
- ^ "Q: What are Windows Server 8's Scalability Numbers?"
. Retrieved November 05, 2011.
- ^ Thurott, Paul. "Q: Will Windows Server 8 require the processor to support SLAT?"
. Retrieved November 05, 2011.
Books
External links